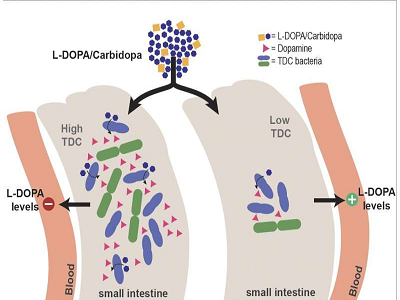
How gut bacteria affect the treatment of Parkinson's disease
Patients with Parkinson's disease are treated with levodopa, which is converted into dopamine, a neurotransmitter in the brain. In a study published on 18 January in the journal Nature Communications, scientists from the University of Groningen show that gut bacteria can metabolize levodopa into dopamine. And since dopamine cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, this makes the medication less effective—even in the presence of inhibitors that should prevent the conversion of levodopa.
Read more...